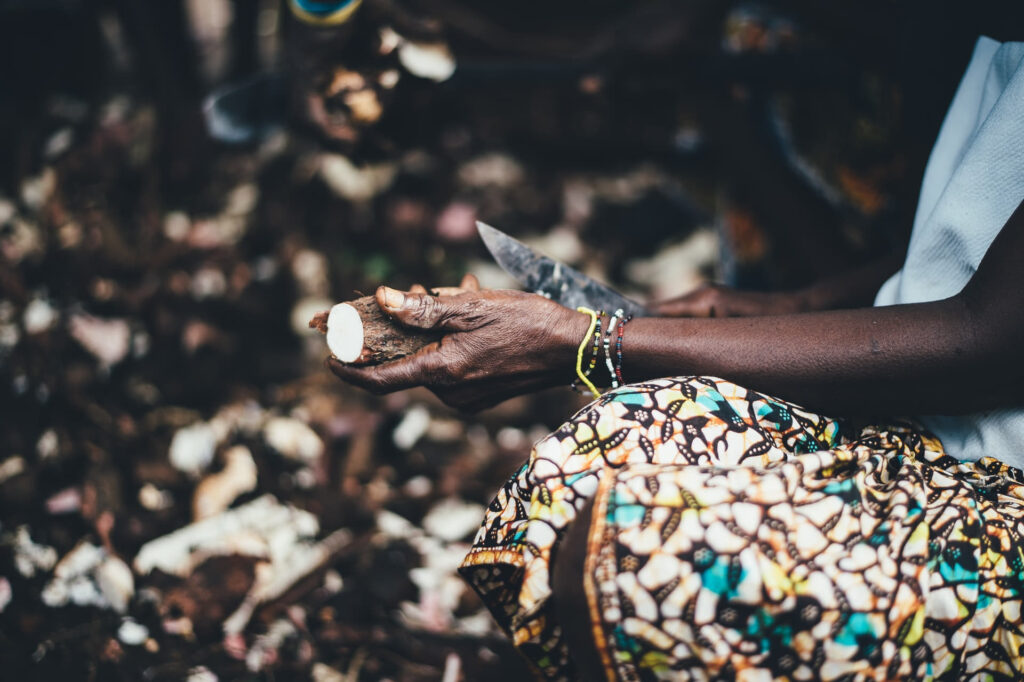
Cassava, also known as Manihot, is an important food in the diet of tropical countries.
It exists in most traditional recipes, as it is valued for its versatility and nutritional quality.
What are the health benefits and uses of the cassava root?
A Few Facts About Cassava
Cassava, also known as Manihot, Yuca, or Manioc, is a deciduous shrub from the poppy family that originated in South America.
However, today most of its growth is done in Africa.
The Manihot shrub has an average height of one meter, and it can reach a height of 3 meters
Its main use is for food due to its starchy tubular root.
Boiled cassava root has a delicate flavor, and can replace boiled potatoes in a variety of dishes.
You can use it to make, among other things, puree, soups, stews, and dumplings.
Tapioca is also made from the starchy flour, which is extracted from the cassava root.
Cassava root is very rich in starch and contains relatively large amounts of calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin C.
What is the Right Way to Use Cassava?

Before using the cassava root, you must peel it.
Moreover, it should always be eaten cooked, since in its raw state it contains toxins that are harmful.
Raw cassava contains substances called cyanogenic glycosides, which release cyanide into the body when ingested.
Excessive consumption of this substance causes cyanide poisoning and in turn, can affect thyroid and nerve function.
Therefore, it should be eaten cooked, in moderation.
If you are in a medical condition, you must consult a doctor or nutritionist before adding the cassava to the diet, in case it has any adverse effect.
The cassava root can be prepared boiled or fried as if it were a potato.
You can serve it as a side dish or as a main meal.
You can also grind it into flour and use it in any recipe.
Cassava is suitable for people with celiac disease since it does not contain gluten.
As for the fresh cassava leaves, they are edible as long as they are cooked.
Like the cassava root, the raw leaves can be toxic.
In addition, Consumption of the leaves compensates for the lack of protein in the root, as the leaves are rich in protein.
Nutritional Benefits of Cassava Root

Much of Cassava’s medicinal properties come from its interesting nutritional profile.
And as reported in a study published in comprehensive reviews on food science and food safety, 100 grams of cooked cassava root contains only 112 calories.
Of these, 98% are carbohydrates and the rest are proteins and fats.
The same publication reveals that cassava is also a source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Among other things, cooked cassava also contains trace amounts of iron, vitamin C, and niacin.
Despite this, its nutritional profile is minimal when comparing it to other root vegetables like beetroots and sweet potatoes.
Health Benefits of Cassava Root
Digestive System
Cassava is easy to digest, therefore those suffering from digestive problems such as gastritis, heartburn, ulcers, or colitis should consume it.
Cassava is a food that can replace grains since it does not contain gluten,
therefore people with celiac disease can use it.
Cassava roots are very similar to potatoes or sweet potatoes and can be cooked in similar ways.
However, the most noticeable difference is that cassava contains more than 90% starch, as it is very low in fat and protein.
In addition, it is a source of polyphenols and tannins, which is prominent in its antioxidant action.
Similarly, its great starch source provides satiety that helps in weight loss and improves metabolism and bowel movements.
Cassava Root Contains Vitamin K Which Protects the Bones
Among the vitamins we can find in this root, stands out Vitamin K which protects the bones and prevents us from developing osteoporosis.
It is also a source of vitamin B, thiamine, vitamin B-6, riboflavin, and pantothenic acid.
Therefore, adding cassava root to the diet helps with joint problems and reduces muscle, bone, and tendon pain.
Benefits of Cassava to the Circulatory System
Cassava contains a high content of resveratrol, which reduces bad cholesterol levels.
Moreover, it significantly improves blood circulation and increases platelet production.
Adding cassava root to the diet can protect from atherosclerosis.
In particular, it facilitates lymph drainage and reduces uric acid excess.
Cassava contains minerals such as zinc, magnesium, and copper.
It is also a good source of potassium, which functions as a regulator of heart rate and blood pressure.
Cassava Root Strengthens the Immune System
The cassava contains nutrients that strengthen the functions of the immune system.
Therefore, the inclusion of this food in the regular diet prevents infectious diseases, allergies, and other conditions often given by a weak immune system.
Among other things, cassava contains saponins.
Saponins are substances that, according to a study published in 2014, have the potential as vaccines.